Secure Your Spring Boot API with Asgardeo
# Secure Your Spring Boot API with Asgardeo
Spring Boot is a Java framework that simplifies the development of robust applications by offering a production-ready environment with minimal configurations. Spring security provides comprehensive tools to facilitate authentication and authorization for REST APIs. Spring Security seamlessly integrates with Spring Boot and allows developers to focus on business logic rather than boilerplate code.
The goal of this tutorial is to explore how we can enhance API security by integrating Asgardeo, a comprehensive identity and access management solution, with Spring Security. This combination will handle authentication and authorization processes effectively.
Let's look at the following example scenario.
# Scenario
Issue Management Application is a REST API service built using Spring Boot and Spring Security. The application allows the following CRUD operations to be performed.
- list issues
- create issues
- update issues
- delete issues
The application users are divided into the following two roles with different levels of permissions.
Reporterscan create and list issues.Fix-Verifiershave full access to the application and can perform all operations.
You are tasked with delegating access to the application so that users are given appropriate levels of access based on their roles. Let's use Asgardeo to achieve this.
# Step 1: Create a simple CRUD API
Create a simple issue management REST API which provides create, view, update and delete operations to issues.
You can find a sample implementation in the following repository (opens new window).
# Step 2: Integrate your service with Asgardeo
Follow the instructions below to connect your Issue Management service with Asgardeo.
# Step 2.1: Register your API resources in Asgardeo
First, let's register your issue management REST API with Asgardeo. To do so,
Go to your organization from the Asgardeo Console (opens new window).
Define permissions for the API resource with the following permissions.
issues:viewissues:createissues:updateissues:delete
# Step 2.2 Register your application in Asgardeo
You need to register your application in Asgardeo and connect your API resources to it. To do so,
Create a standard-based application in Asgardeo by selecting the grant type as
Codeand the access token type asJWT.Connect the API resources with the application that you created in Step 1 above.
# Step 2.3 Create roles in your application
Let's define the various roles of your application and give each role appropriate permissions.
To do so, create application roles with the following details:
- Reporter - Assign
create:issesandview:issuespermissions. - Fix-Verifier - Assign all permissions.
# Step 2.4 Assign roles to user groups in Asgardeo
For the application roles defined in Step 2.3 above to take effect, we need to assign those roles to users in Asgardeo. The best way to do this is to create user groups and assign the relevant roles to each group.
To do so,
Create user groups in Asgardeo. For this scenario, let's create two groups and name them
ReporterandFix-Verifier.Assign application roles created in step 2.3 above to the relevant groups.
# Step 2.5 Assign users to groups in Asgardeo
Now that you have assigned the application roles to the relevant user groups in Asgardeo, let's add users to these groups so that they can access the API resources.
To do so,
# Step 3: Configure Spring Security
In your Spring project, do the following configurations so that it is correctly integrated with Asgardeo.:
Create a security configuration file and include the following JWT decoder to validate Asgardeo issued tokens.
Asgardeo issues access tokens of
at+jwttype.NimbusJwtDecoder jwtDecoder = NimbusJwtDecoder.withJwkSetUri(jwkSetUri).jwtProcessorCustomizer(customizer -> { customizer.setJWSTypeVerifier(new DefaultJOSEObjectTypeVerifier<>(new JOSEObjectType("at+jwt"))); }) .build();1
2
3
4Add the following annotation to each endpoint that needs to be restricted with a scope.
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('<scope>’)")1For example, if the endpoint requires the
issues:viewscope, add the following annotation.@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('issues:view')")1
# Step 4: Try it out
Let's try to access the API resources of the sample application as a Reporter user and a Fix-Verifer user. Follow the steps below to try out the scenario.
Use a web browser to obtain an authorization code using the URL shown below.
Refer the documentation to learn about the authorization code flow.
https://api.asgardeo.io/t/{organization_name}/oauth2/authorize ?response_type=code &client_id={client_id} &redirect_uri={redirect_uri} &scope=issues:create+issues:delete+issues:update+issues:view1
2
3
4
5Log in as a
Reporteruser to Asgardeo and provide consent to the application to access the shown scopes.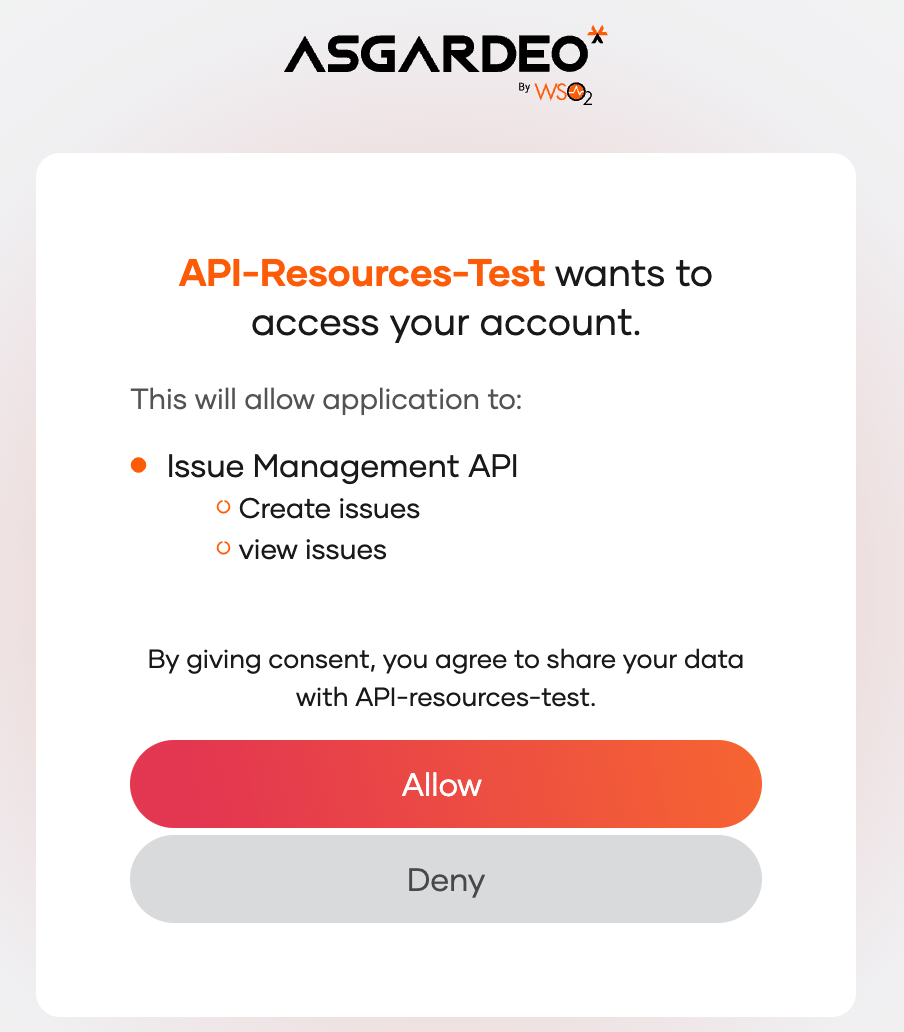
Once you retrieve the authorization code from the browser response, use the following cURL command to request for an access token.
curl --location --request POST 'https://api.asgardeo.io/t/{organization_name}/oauth2/token' --header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' --data-urlencode 'code={authorization_code}' --data-urlencode 'grant_type=authorization_code' --data-urlencode 'client_id={client_id}' --data-urlencode 'client_secret={client_secret}' --data-urlencode 'redirect_uri={redirect_uri}'1
2
3
4
5
6
7Observe the scopes calim in the access token and verify that the
Reporteruser has access to onlyissues:viewandissues:createscopes.Repeat steps 1-4 for a
Fix-Verifieruser and observe that this user has access to all scopes.Start the sample application and invoke a restricted API using each of the tokens you obtained above.
- The
Reportertoken will only allow viewing and creating issues in the system. - The
Fix-Verifiertoken will enable viewing, creating, updating, and deleting issues in the system.
- The
