Implement private key JWT client authentication for OIDC
# Implement private key JWT client authentication for OIDC
See the instructions below to implement private key JWT (JSON Web Token) client authentication for your OIDC application. This method can be used for confidential client applications that are implemented on secure servers. These clients must identify themselves with the token endpoint of Asgardeo (authorization server) before acquiring an access token.
Typically, when you implement a grant type using OIDC in an application, there are several ways to implement client authentication at the token endpoint. With private key JWT client authentication, the client application uses a JWT to identify itself to the token endpoint. Note that the following two parameters are sent in the token request for this purpose: client_assertion_type = urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer
and the JWT that is set as the client_assertion.
See the list of client authentication methods in the OIDC specification (opens new window).
Listed below are the high-level steps in the private key JWT client authentication process.
- Prepare a private key and public key pair for the client.
- Prepare the JSON payload and sign it using the client's private key.
- Share the public key with the authorization server (Asgardeo).
- Client application sends the JWT and the signature in the token request to the authorization server.
- The authorization server verifies the JWT using the public key.
- The authorization server extracts the signature using the public key and authenticates the client.
- The access token is granted if the client is successfully authenticated.
Follow the steps given below to implement private key JWT client authentication.
# Register the client app in Asgardeo
Register the client application in Asgardeo as follows:
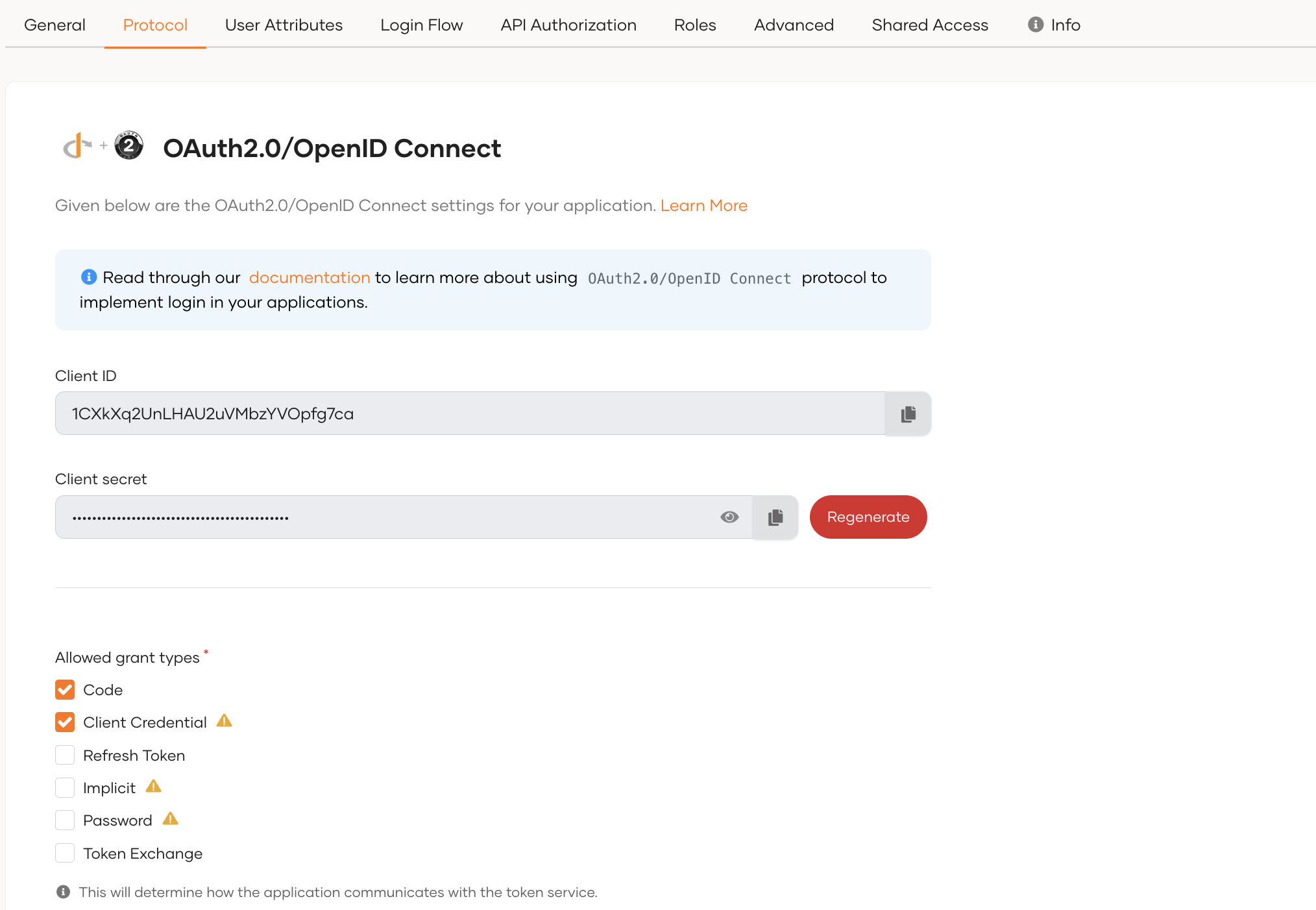
Create an OIDC application:
Go to the Protocol tab of the new application and configure the required grant type.
# Prepare the private key and public key
Generate a public key and private key for the client application. Follow the steps given below.
Open a terminal and execute the following keytool command to create the client keystore.
Replace the following values:
<clinet_ID>: Specify the client ID generated when registering the client application in Asgardeo.<keystore_name>: Specify the name of the keystore you are creating.
keytool -genkey -alias <client_ID> -keyalg RSA -keystore <keystore_name>.jks1Convert the
.jkskeystore toPKCS#12format.Replace
<dest_keystore_name>to specify a name for the new keystore inPKCS#12format.keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore <keystore_name>.jks -destkeystore <dest_keystore_name>.p12 -deststoretype PKCS121Export the public key from the
.p12keystore.Replace
<pub_key_name>to specify a name for the public key certificate file.openssl pkcs12 -in <dest_keystore_name>.p12 -nokeys -out <pub_key_name>.pem1Export the private key from the
.p12keystore.Replace
<private_key_name>to specify a name for the private key certificate file.openssl pkcs12 -in <dest_keystore_name>.p12 -nodes -nocerts -out <private_key_name>.pem1
# Upload the public key to Asgardeo
Go to the Certificate section in the Protocol tab of your application registered in Asgardeo and add the public key certificate of your client application.
See the instructions on adding certificates to applications.
# Prepare the JWT payload
Prepare the JSON payload required by the authorization server for client authentication. Given below is a sample payload with only the required data. The complete list of required and optional claims that can be used is defined in the OpenID Connect specification (opens new window).
Note that the audience (aud) is the token endpoint URL of the authorization server, and the issuer (iss) and the subject (sub) is the client ID generated for your application by the authorization server in the previous step.
{
"iss": "RN0I55bldQftY97uNq9iIXQA21wa",
"sub": "RN0I55bldQftY97uNq9iIXQA21wa",
"exp": 1643650350,
"iat": 1643650346,
"jti": "10003",
"aud": "https://api.asgardeo.io/t/<organization_name>/oauth2/token"
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Once you have created the payload, generate a signature for it using the client application's private key. This JWT is known as the client_assetion.
# Get the access token
Listed below are the main steps for invoking the token endpoint and acquiring an access token using the JWT.
Client application sends the JWT and the signature in the token request to the authorization server.
Note the following two parameters that should be set in the token request:
client_assertion: The authentication token (JWT assertion) must be sent as the value of this parameter.client_assertion_type: The value of this parameter must beurn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer.
The authorization server verifies the JWT using the public key.
Authorization server extracts the signature using the public key and authenticates the client.
The access token is granted if the client is successfully authenticated.
Let’s look at how this works for different grant types.
# Authorization code flow
If you are implementing the authorization code flow, you have enabled code as the grant type when registering your application. You can now send the following requests to get the access token.
First, invoke the authorization endpoint in Asgardeo and get an authorization code.
https://api.asgardeo.io/t/<organization_name>/oauth2/authorize?scope={scope}&response_type=code&redirect_uri={redirect_uri}&client_id={client_id}1Invoke the token endpoint and get the access token.
curl --location --request POST 'https://api.asgardeo.io/t/{organization_name}/oauth2/token' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ --data-urlencode 'code={authorization_code}' \ --data-urlencode 'grant_type=authorization_code' \ --data-urlencode 'client_assertion_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer'\ --data-urlencode 'client_assertion={jwt_assertion}' \ --data-urlencode 'redirect_uri={redirect_uri}'1
2
3
4
5
6
7Be sure to replace the following values in the request:
{organization_name}Name of the organization that you are accessing. {authorization_code}The authorization code that was received by invoking the authorization endpoint. {jwt_assertion}The JWT assertion that was created for your client application. {redirect_uri}The callback URL of your client application.
# Client credential flow
If you are implementing the client credentials flow, you have enabled client credentials as the grant type when registering your application. You can now send the following requests to get the access token.
curl --location --request POST 'https://api.asgardeo.io/t/<organization_name>/oauth2/token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data-urlencode 'grant_type=client_credentials’ \
--data-urlencode 'client_assertion_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer'\
--data-urlencode 'client_assertion={jwt_assertion}’
2
3
4
5
Be sure to replace the following values in the request:
{organization_name} | Name of the organization that you are accessing. |
|---|---|
{jwt_assertion} | The JWT assertion that was created for your client application. |
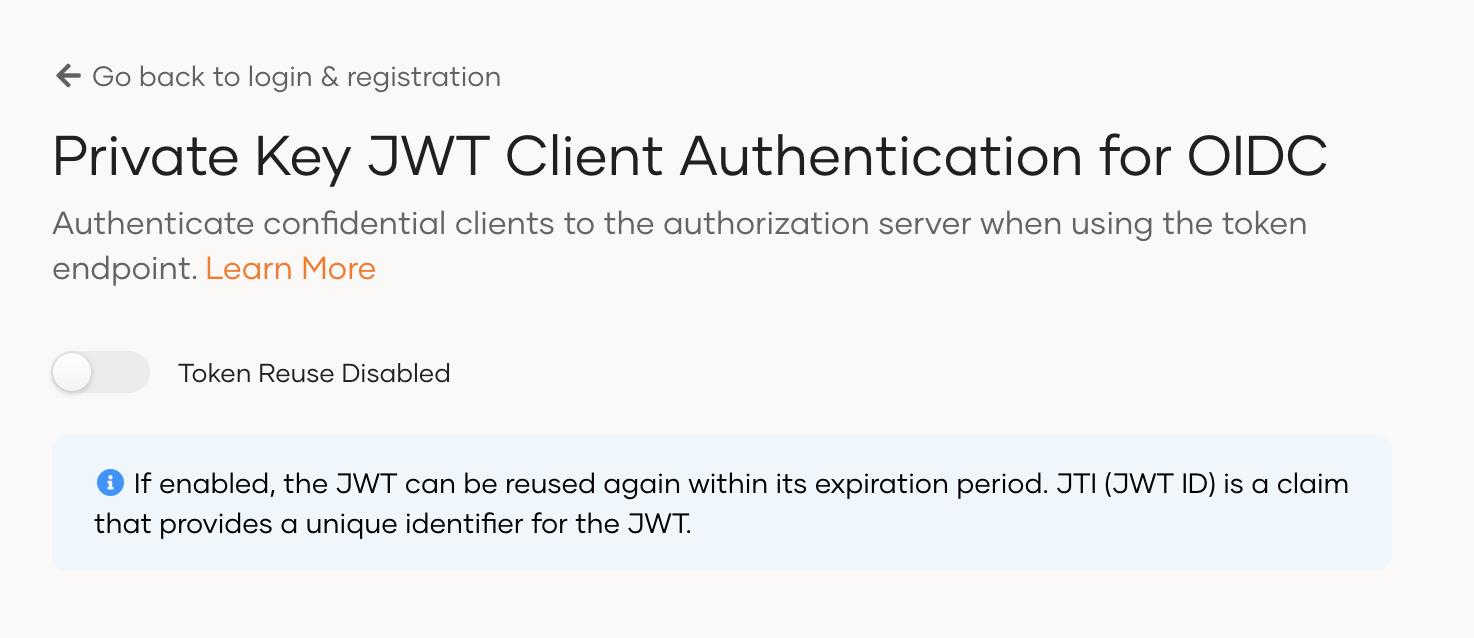
# Reuse tokens (optional)
The jti (JWT ID) claim is a unique identifier included in the JWT token, which controls the reuse of the access token. By default, token reuse is disabled in Asgardeo. If you enable token reuse, the jti can be reused within its expiration period.
To enable token reuse in Asgardeo.
On the Asgardeo Console, go to Login & Registration.
Under Login Security, click Private Key JWT Client Authentication (OIDC).
Switch on the toggle to enable token reuse.